Interpretation Methods for New Landslides
Selecting cloud-free satellite or aerial images from two periods before and after the disaster, and manually outlining areas of obvious surface landslide changes through comparison.
Digitizing and outlining landslide areas manually based on image resolution and interpretation requirements.
Sources of Imagery Data Used
Diverse Satellite Imagery Combined with Aerial Photography
- Sentinel-2
- Planet
- SPOT
- Pleiades
- Formosat-5
- Aerial Photos from the Forestry and Nature Conservation Agency, Ministry of Agriculture
Interpretation Scope and Results Presentation
Interpretation content includes seismic intensity of 5 Strong (inclusive) or above full detection, to grasp the status of new landslides and areas at risk of disaster.
Case Study: Hualien Earthquake (2024/04/03)
- Number of New Landslide Locations: 1,391 (locations)
- Total Area: Approximately 943.76 (hectares)
- Located in Debris Flow Potential Stream Catchment Areas: 444 (locations)
- Near Railways and Highways: 62 (locations)
Interpretation Standards and Limitations
Minimum Interpretation Area
- If the landslide area is less than 0.1 (hectares), it is not classified as a new landslide.
Challenging Factors
- High cloud cover affects image quality and completeness
- Geometric errors and time differences in past image data
- High-altitude cloud shadows or extreme terrain increase interpretation difficulty
Landslide Investigation Data
In addition to conducting irregular disaster event investigations for landslide areas, the Soil and Water Conservation Agency, Ministry of Agriculture (SWCA) conducts detailed landslide investigations for specific areas annually to grasp the potential and risk of landslide occurrence.
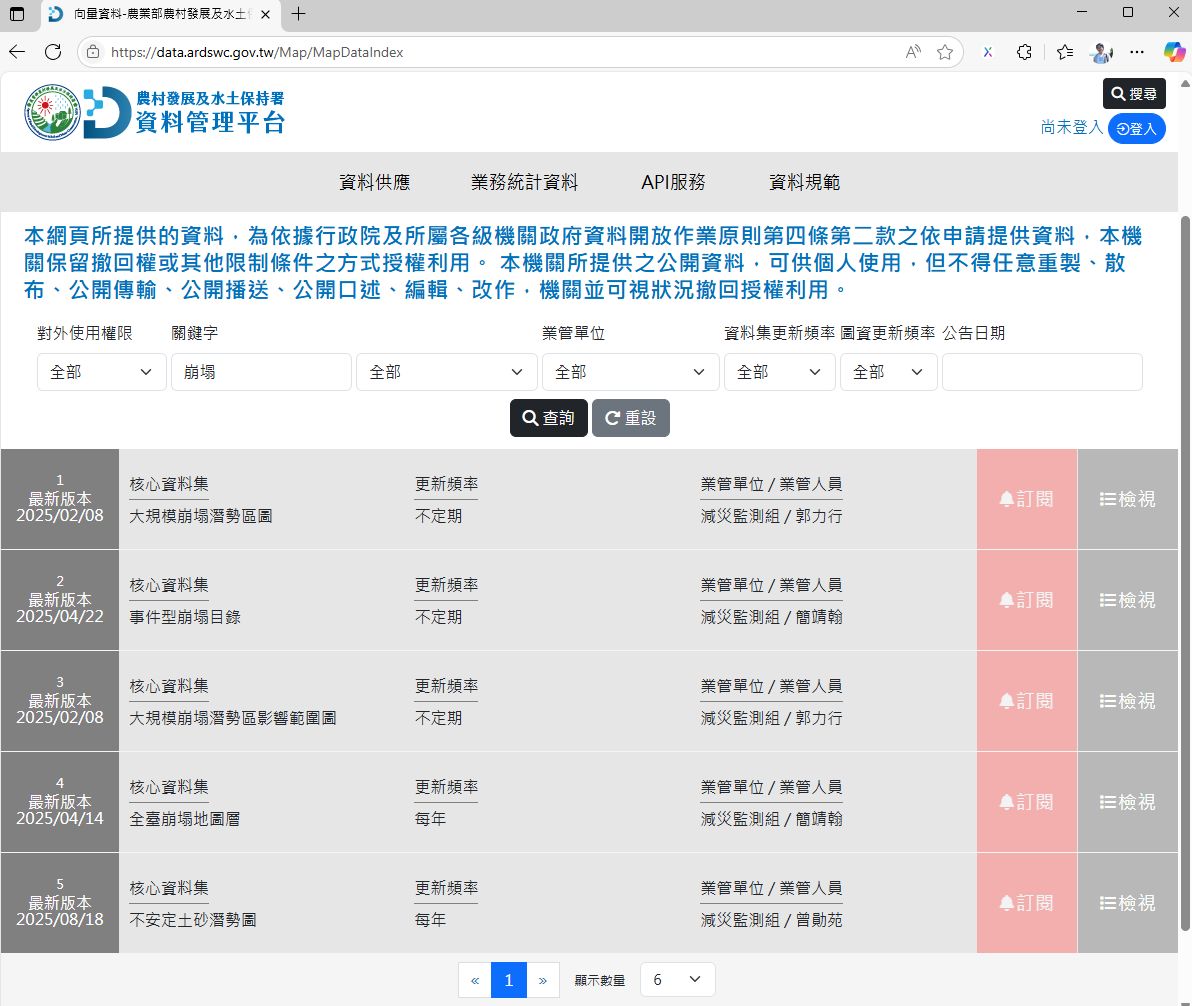
The investigation results will be compiled into maps and published on the SWCA Data Management Platform , for use by relevant units in disaster prevention planning and emergency response operations.
Core Landslide Area Datasets Released by SWCA
The SWCA currently releases 5 core datasets related to landslide areas for public download or application for use:
- 1. Large-Scale Landslide Potential Area Map
- 2. Event-Based Landslide Catalog
- 3. Large-Scale Landslide Potential Area Impact Range Map
- 4. Taiwan-wide Landslide Layer Map
- 5. Unstable Sediment Potential Map
Spatial Presentation of Landslide Investigation Results
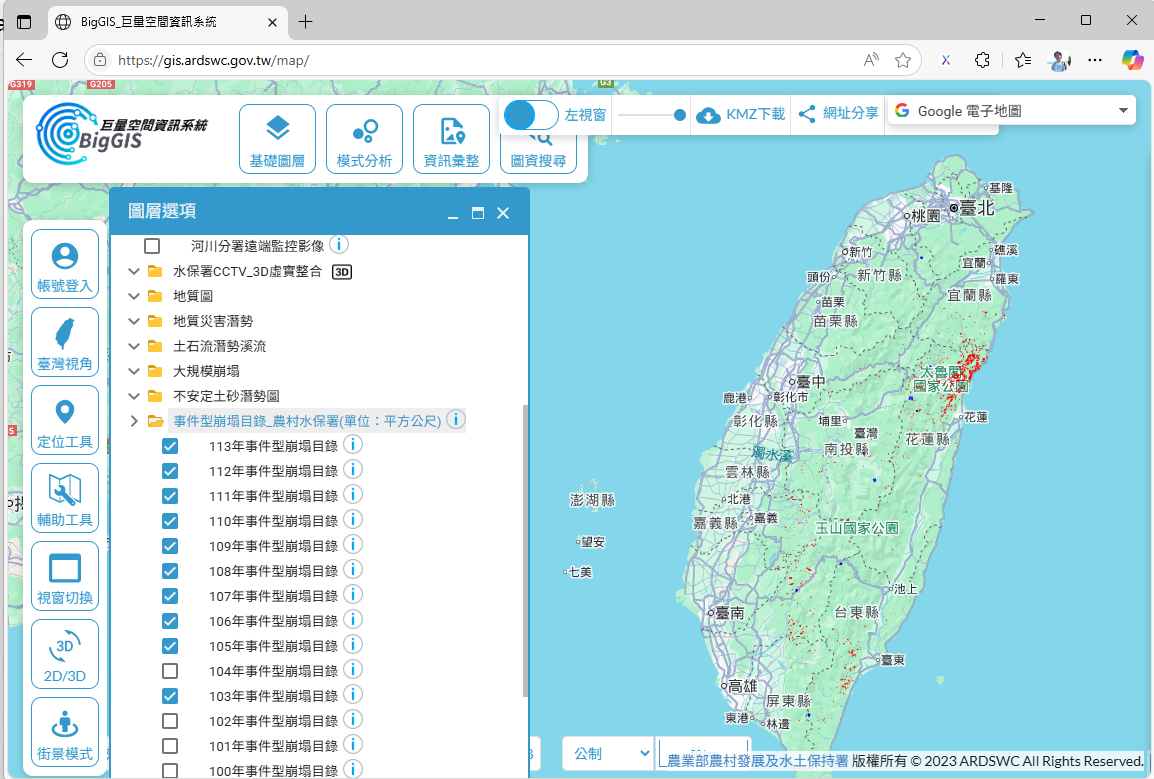
The "Big Geographic Information System (BigGIS)" established by the SWCA integrates multi-source remote sensing imagery and monitoring data to provide diverse geographic information services. Among them, the landslide area layer can show the scope and distribution of new landslides interpreted after each disaster, combined with essential data such as debris flow potential streams, topography, and transportation networks, helping to assess the disaster impact range and potential risks, serving as an important basis for post-disaster response, recovery, reconstruction, and disaster prevention/reduction decisions.
Website Links
SWCA Big Geographic Information System (BigGIS)
Provides geographic information query and application related to large-scale landslides and soil/water conservation.
Go to BigGIS